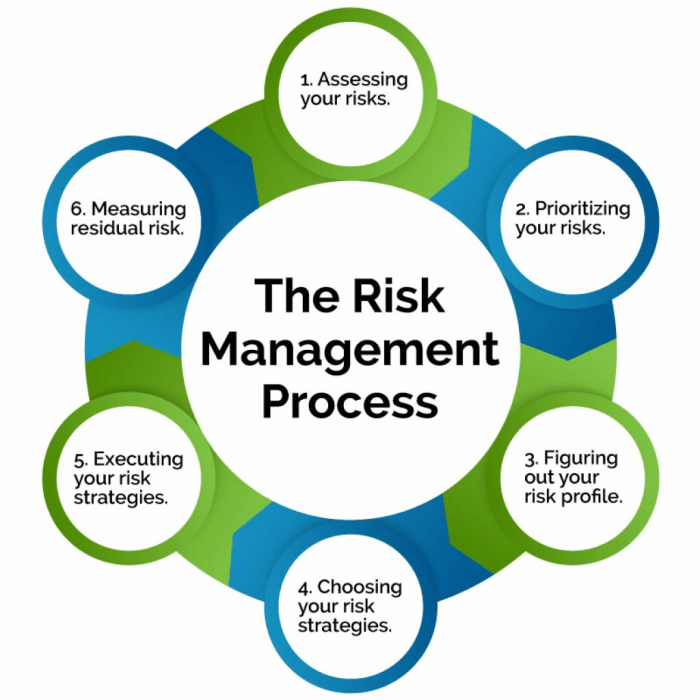
Exploring the realm of Risk Management Models unveils a world of strategic frameworks and tools designed to navigate and reduce potential risks across various industries. From assessing risks to implementing tailored strategies, this topic delves into the core principles and practices essential for effective risk management.
As organizations strive to anticipate and address risks proactively, understanding the nuances of risk management models becomes paramount for sustainable growth and success.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is a crucial component of risk management models as it helps identify, evaluate, and prioritize potential risks that could impact an organization’s objectives. By conducting a thorough risk assessment, businesses can make informed decisions to mitigate or manage these risks effectively.
Key Steps in Conducting Risk Assessment
- Identify and define the scope of the risk assessment, including the objectives and criteria.
- Gather relevant data and information on potential risks, such as historical data, industry trends, and internal processes.
- Analyze and evaluate the identified risks based on their likelihood of occurrence and potential impact.
- Assess the existing controls and mitigation measures in place to address the identified risks.
- Prioritize risks based on their severity and develop a risk treatment plan to address them effectively.
Tools and Methods for Risk Assessment
- SWOT Analysis: A strategic planning tool used to identify the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats facing an organization.
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): A systematic approach to identify and prioritize potential failure modes in a process and their effects.
- Quantitative Risk Analysis: Using mathematical models and statistical techniques to quantify risks based on probability and impact.
- Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP): A systematic preventive approach to food safety that identifies, evaluates, and controls hazards throughout the food production process.
Risk Management
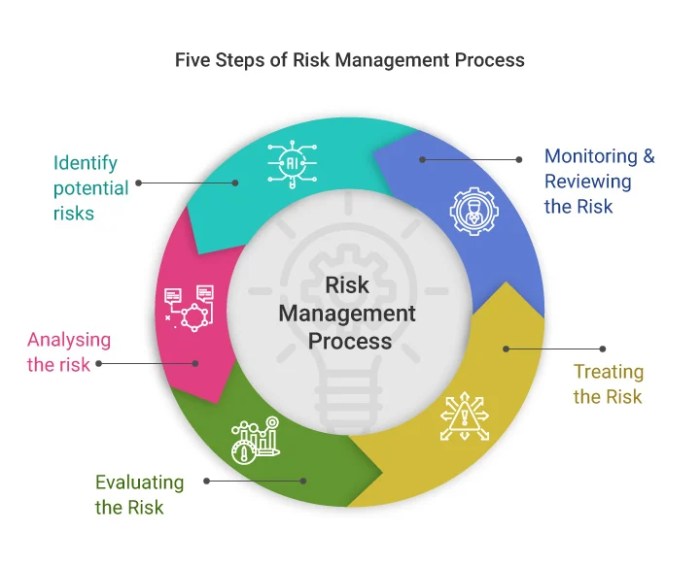
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks, followed by coordinating and applying resources to minimize, monitor, and control the probability or impact of unfortunate events. It differs from risk assessment in that while risk assessment focuses on identifying and evaluating potential risks, risk management goes a step further by developing strategies to address and mitigate those risks.
Components of an Effective Risk Management Plan
An effective risk management plan typically includes the following components:
- Identification of Risks: This involves identifying potential risks that could affect the organization’s objectives.
- Assessment of Risks: Once risks are identified, they are assessed in terms of their likelihood and potential impact.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: Developing strategies to minimize or eliminate the identified risks.
- Monitoring and Controlling Risks: Regular monitoring and control measures to ensure the effectiveness of risk management efforts.
- Communication and Reporting: Clear communication and reporting of risks, mitigation strategies, and progress to relevant stakeholders.
Successful Risk Management Strategies in Organizations
Several organizations have implemented successful risk management strategies to mitigate potential risks and protect their operations. One notable example is the airline industry, which employs rigorous safety protocols and training programs to minimize the risk of accidents. Another example is financial institutions that use sophisticated risk management models to monitor and mitigate financial risks such as market fluctuations and credit defaults.
Risk Tolerance

Risk tolerance refers to the level of risk that an organization or individual is willing to accept in pursuit of their objectives. In the context of risk management models, understanding risk tolerance is crucial as it helps in determining the acceptable level of risk exposure and guides decision-making processes.
Variability Across Industries and Organizations
Different industries and organizations have varying levels of risk tolerance based on factors such as their goals, financial stability, regulatory environment, and risk appetite. For example, a tech startup may have a higher risk tolerance as they aim for rapid growth and innovation, while a government agency may have a lower risk tolerance due to the need for stability and security in their operations.
Influencing Decision-making
Risk tolerance directly impacts decision-making processes within a company by shaping how risks are identified, assessed, and managed. For instance, a company with a high risk tolerance may be more inclined to invest in high-risk ventures with the potential for high returns, while a company with a low risk tolerance may prioritize conservative strategies to ensure stability and minimize potential losses.
Risk Management Models
When it comes to managing risks effectively, organizations often rely on various risk management models to guide their strategies. These models provide a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks, ultimately helping organizations achieve their objectives while minimizing potential threats.
COSO ERM Framework
The COSO ERM (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission Enterprise Risk Management) framework is a widely recognized model that helps organizations integrate risk management into their overall strategic planning and decision-making processes. It focuses on aligning risk appetite with strategy, enhancing risk response decisions, reducing operational surprises, and identifying and managing risks across the organization.
ISO 31000
ISO 31000 is an international standard that provides guidelines and principles for effective risk management. It emphasizes the importance of a systematic and proactive approach to managing risks, incorporating risk identification, assessment, treatment, monitoring, and communication. ISO 31000 aims to help organizations create value and improve their performance by managing risks in a coordinated and structured manner.
Comparison of Risk Management Models
- The COSO ERM framework focuses on integrating risk management into strategic planning, while ISO 31000 provides guidelines for a systematic risk management approach.
- COSO ERM emphasizes aligning risk appetite with strategy, whereas ISO 31000 highlights the importance of creating value through effective risk management.
Choosing the Right Model
Organizations should consider their specific needs, objectives, industry requirements, and risk tolerance levels when selecting a risk management model. It is essential to choose a model that aligns with the organization’s goals and culture, enabling effective risk management practices that drive sustainable growth and resilience.
In conclusion, Risk Management Models serve as crucial roadmaps for organizations to steer through uncertainties and challenges, fostering resilience and adaptability in a dynamic business landscape. By embracing robust risk assessment, management, and tolerance practices, businesses can proactively safeguard their interests and thrive amidst evolving risks.
FAQs
How do risk management models benefit organizations?
Risk management models provide a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and minimize potential threats effectively.
What role does risk tolerance play in risk management models?
Risk tolerance influences how organizations perceive and respond to risks, shaping their decision-making processes and risk management strategies to align with their objectives and industry standards.





