Embark on a journey into the world of operational risk management best practices, where businesses navigate challenges with strategic finesse and resilience. Explore key insights and effective strategies in this captivating narrative.
Operational Risk Management Best Practices
Operational risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that result from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, systems, or external events. It is essential for businesses to proactively manage these risks to prevent financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory issues.
Importance of Operational Risk Management
Operational risk management is crucial for businesses as it helps in maintaining operational efficiency, ensuring compliance with regulations, protecting the organization’s reputation, and safeguarding financial stability. By identifying and addressing potential risks, businesses can reduce the likelihood of disruptions and improve overall performance.
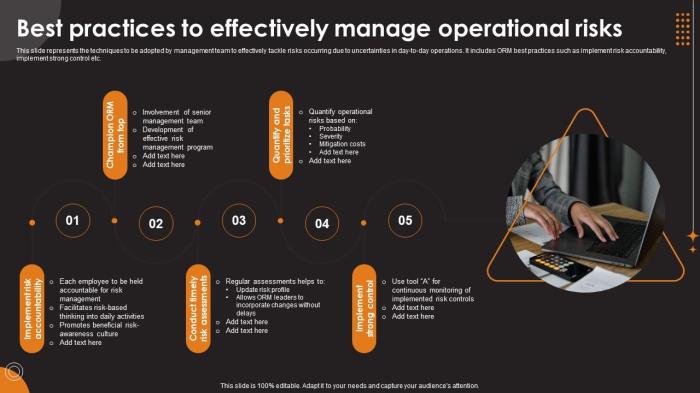
- Implementing robust internal controls to prevent errors and fraud.
- Conducting regular risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Training employees on risk management practices to create a risk-aware culture.
- Establishing contingency plans to address unexpected events and minimize their impact.
Effective operational risk management can enhance decision-making processes, increase resilience to market changes, and improve overall business performance.
Differences from Other Types of Risk Management
Operational risk management differs from other types of risk management such as credit risk or market risk, as it focuses on internal processes and controls rather than external factors. While credit risk deals with the potential for financial loss due to a borrower’s failure to repay a loan, operational risk addresses risks associated with the day-to-day operations of the organization.
- Credit risk involves assessing the creditworthiness of borrowers, while operational risk assesses the effectiveness of internal controls.
- Market risk relates to fluctuations in market prices, while operational risk deals with errors or failures in processes.
- Operational risk management is more proactive in nature, focusing on prevention rather than mitigation after an event occurs.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is a crucial component of operational risk management that involves identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential risks that could impact an organization’s operations. By conducting risk assessments, organizations can proactively identify vulnerabilities and implement appropriate mitigation strategies to minimize the likelihood of adverse events.
Common Methods and Tools for Conducting Risk Assessments
- Interviews with key stakeholders: Engaging with employees, managers, and other relevant parties to gather insights on potential risks.
- Surveys and questionnaires: Collecting data from a wider group of individuals to assess the likelihood and impact of various risks.
- Historical data analysis: Reviewing past incidents and near-misses to identify recurring patterns and trends.
- Scenario analysis: Creating hypothetical scenarios to simulate potential risks and evaluate their potential impact on the organization.
- Risk registers and matrices: Documenting identified risks and assessing their likelihood and impact using risk assessment tools.
Role of Risk Assessment in Identifying Potential Operational Risks
Risk assessment plays a critical role in helping organizations identify and prioritize potential operational risks. By systematically evaluating different risk factors, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of the threats they face and develop targeted risk management strategies. Additionally, risk assessments enable organizations to allocate resources effectively, implement appropriate controls, and continuously monitor and review their risk landscape to ensure operational resilience.
Risk Management Strategies

Effective risk management strategies are crucial for organizations to identify, assess, and mitigate operational risks. Prioritizing operational risks based on their impact and likelihood is essential in allocating resources effectively. Risk mitigation plays a key role in reducing the impact and likelihood of risks, ensuring the organization’s resilience and sustainability.
Prioritizing Operational Risks
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify and evaluate potential operational risks.
- Rank risks based on their potential impact on the organization’s objectives and likelihood of occurrence.
- Consider external factors, such as regulatory changes or market trends, that may affect the prioritization of risks.
Risk Mitigation and Importance
- Develop a risk mitigation plan that Artikels specific actions to reduce the impact and likelihood of identified risks.
- Implement controls and measures to monitor and manage operational risks effectively.
- Regularly review and update the risk mitigation plan to address new risks and changing circumstances.
Risk Tolerance

Risk tolerance is the level of risk that an organization is willing to accept or take on in pursuit of its objectives. It plays a crucial role in operational risk management as it helps organizations make informed decisions regarding risk-taking activities.
Significance of Risk Tolerance
Determining risk tolerance levels is essential for organizations to establish boundaries within which they can operate safely and effectively. It allows them to strike a balance between risk and reward, ensuring that they do not expose themselves to unacceptable levels of risk.
- Organizations assess their risk tolerance by considering factors such as their financial capacity, regulatory requirements, and overall risk management framework.
- By clearly defining their risk tolerance, organizations can align their risk management strategies and decisions with their overall business objectives.
- Understanding risk tolerance levels helps organizations prioritize resources and focus on managing risks that fall within their acceptable risk thresholds.
Relationship between Risk Tolerance and Risk Appetite
Risk tolerance is closely related to risk appetite, which represents the amount and type of risk an organization is willing to pursue or retain to achieve its objectives. While risk appetite sets the overall tone for risk-taking, risk tolerance defines the specific limits within which risks can be managed.
Organizations with a high risk appetite may have a higher risk tolerance, allowing them to engage in riskier activities to pursue greater rewards. On the other hand, organizations with a low risk appetite will have a lower risk tolerance and may avoid certain types of risk altogether.
In conclusion, operational risk management best practices serve as a cornerstone for sustainable business growth, offering a roadmap to mitigate risks and enhance operational efficiency. Dive into these essential guidelines to steer your organization towards success.
General Inquiries
What is the significance of operational risk management?
Operational risk management is crucial for businesses to identify, assess, and mitigate risks that could impact their operations, financial stability, and reputation.
How do organizations determine their risk tolerance levels?
Organizations assess their risk tolerance by considering factors such as business objectives, regulatory requirements, financial health, and stakeholder expectations.
What are effective strategies for managing operational risks?
Effective strategies include risk assessment, risk prioritization, risk mitigation planning, regular monitoring, and adapting to changing risk landscapes.





