Exploring the realm of ISO standards for risk management, this introduction sets the stage for a deep dive into the intricacies of risk assessment, management, and tolerance. It aims to captivate readers with a blend of informative insights and engaging content.
As we navigate through the various facets of risk management, we uncover the essence of ISO standards and their pivotal role in ensuring organizational resilience and success.
ISO Standards for Risk Management
ISO standards play a crucial role in guiding organizations in managing risks effectively. These standards provide a framework and best practices to identify, assess, and mitigate risks in various industries.
Key Components of ISO 31000
- Establishing the context: Understanding the internal and external factors that can impact an organization’s objectives.
- Risk assessment: Identifying risks, analyzing their potential impact, and evaluating the likelihood of occurrence.
- Risk treatment: Developing strategies to address and mitigate risks, including risk transfer, avoidance, reduction, or acceptance.
- Monitoring and review: Continuously monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of risk management processes and making improvements as needed.
Comparison of Different ISO Standards
- ISO 31000: Provides principles and guidelines for risk management.
- ISO 27001: Focuses on information security management and includes risk management as a key component.
- ISO 9001: Quality management system standard that also integrates risk management principles.
Examples of Industries Requiring Adherence to ISO Standards for Risk Management
- Healthcare: Ensuring patient safety and data security.
- Finance: Managing financial risks and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Manufacturing: Addressing operational risks and ensuring product quality.
Risk Assessment

Risk assessment is a crucial process within risk management that involves identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential risks that may impact an organization’s objectives. By conducting a thorough risk assessment, organizations can better understand their risk landscape and make informed decisions to mitigate or avoid potential threats.
Steps in Conducting a Thorough Risk Assessment
- Identifying Risks: The first step involves identifying all possible risks that could affect the organization’s operations, assets, or goals.
- Analyzing Risks: Once identified, each risk must be analyzed to determine its potential impact and likelihood of occurrence.
- Evaluating Risks: Risks are then evaluated based on their severity and the organization’s tolerance level for risk.
- Developing Risk Mitigation Strategies: After evaluating risks, organizations can develop strategies to mitigate, transfer, or accept the identified risks.
Role of Risk Assessment in Identifying Threats and Vulnerabilities
Risk assessment plays a crucial role in identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities that could compromise an organization’s security, financial stability, or reputation. By systematically assessing risks, organizations can proactively address weaknesses in their systems or processes and implement measures to strengthen their resilience against potential threats.
Risk Assessment for Prioritizing Risks
- By conducting a risk assessment, organizations can prioritize risks based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence.
- This prioritization helps organizations allocate resources effectively and focus on addressing the most critical risks first.
- Risk assessment enables organizations to develop a risk management plan that targets high-priority risks and ensures that mitigation efforts are aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Risk Management
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks in order to minimize, monitor, and control the impact of uncertain events on an organization. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the success and sustainability of businesses by helping them anticipate potential threats and opportunities.
Strategies and Techniques
Effective risk management involves a variety of strategies and techniques to mitigate risks. Some common approaches include:
- Risk Identification: This involves identifying and defining potential risks that could affect the organization’s objectives.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and impact of identified risks to prioritize them based on their significance.
- Risk Mitigation: Developing and implementing strategies to reduce the likelihood or impact of risks through preventive measures.
- Risk Monitoring: Continuously monitoring and reviewing risks to ensure that the mitigation strategies are effective.
Tools and Software
There are various tools and software commonly employed in risk management processes to streamline and enhance decision-making. Some examples include:
- Risk Registers: A document used to record and track identified risks, their potential impact, and mitigation strategies.
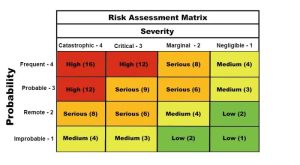
- Risk Assessment Matrix: A visual tool that helps prioritize risks based on their likelihood and impact.
- Monte Carlo Simulation: A statistical technique used to model the impact of different variables on risk outcomes.
- Risk Management Software: Platforms that facilitate the centralization of risk data, analysis, and reporting for better decision-making.
Role in Decision-Making and Strategic Planning
Risk management plays a critical role in decision-making and strategic planning by providing valuable insights into potential risks that could impact the organization’s objectives. By integrating risk management processes into decision-making, businesses can make informed choices that consider both opportunities and threats, leading to more robust strategic plans and sustainable growth.
Risk Tolerance

Risk tolerance is the level of risk that an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives. It plays a crucial role in guiding risk management practices and decision-making processes within an organization.
Determining Risk Tolerance Levels
Determining risk tolerance levels involves a thorough assessment of various factors such as the organization’s objectives, industry regulations, financial capabilities, and stakeholder expectations. Organizations often conduct risk assessments to evaluate the potential impact of risks on their operations and set appropriate risk tolerance levels accordingly.
- Organizational Objectives: The alignment of risk tolerance with organizational objectives is essential to ensure that risks are managed in a way that supports the achievement of strategic goals.
- Regulatory Environment: Compliance with industry regulations and standards can influence the level of risk that an organization is willing to tolerate.
- Financial Considerations: The financial health of an organization, including factors such as budget constraints and cash flow, can impact its risk tolerance.
- Stakeholder Expectations: The expectations of stakeholders, including shareholders, customers, and employees, can also shape an organization’s risk tolerance levels.
Impact on Business Operations
The level of risk tolerance adopted by an organization can have significant implications for its business operations and decision-making processes.
- Strategic Planning: Risk tolerance influences strategic planning initiatives by guiding the allocation of resources and the identification of opportunities and threats.
- Investment Decisions: Organizations with higher risk tolerance levels may be more willing to pursue investment opportunities that offer higher returns but come with greater risks.
- Operational Resilience: Understanding risk tolerance helps organizations build resilience by anticipating and preparing for potential risks that fall within their accepted risk thresholds.
In conclusion, the journey through ISO standards for risk management unveils a mosaic of strategies, tools, and insights that organizations can leverage to navigate uncertain terrains with confidence and competence.
Commonly Asked Questions
How do ISO standards benefit risk management practices?
ISO standards provide a framework for organizations to streamline their risk management processes, enhance decision-making, and improve overall resilience.
What are the key differences between ISO 31000 and other ISO standards for risk management?
ISO 31000 focuses on providing principles and guidelines for risk management, while other ISO standards may have specific industry applications or requirements.
How can organizations effectively determine their risk tolerance levels?
Organizations can assess their risk tolerance by considering factors such as financial capacity, strategic objectives, and industry regulations.
What role does risk assessment play in prioritizing risks for mitigation?
Risk assessment helps organizations identify and evaluate potential risks, allowing them to prioritize mitigation efforts based on the level of impact and likelihood.